
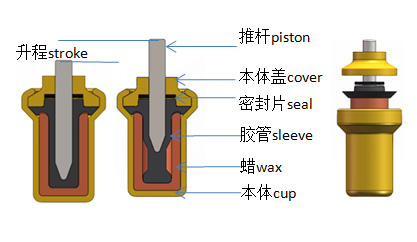
Squeeze-push element
When heated, the wax in the cup expands and the pressure applies, via the sleeve, both a radial force and an axial force on the piston.
Again, an external spring ensures the return of the piston when the temperature decreases.
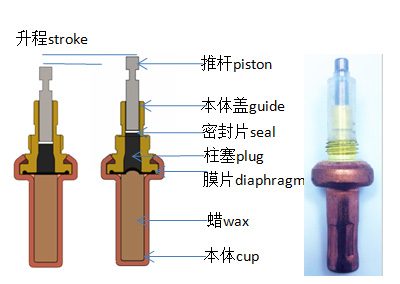
Flat diaphragm element
When heated, the wax enclosed in the cup, expands and pushes against the diaphragm, the movement is transmitted via the plug to the piston. The guide maintains the diaphragm, and allows the plug and piston to slide freely.
An external spring ensures the return of the Piston when cooling down.
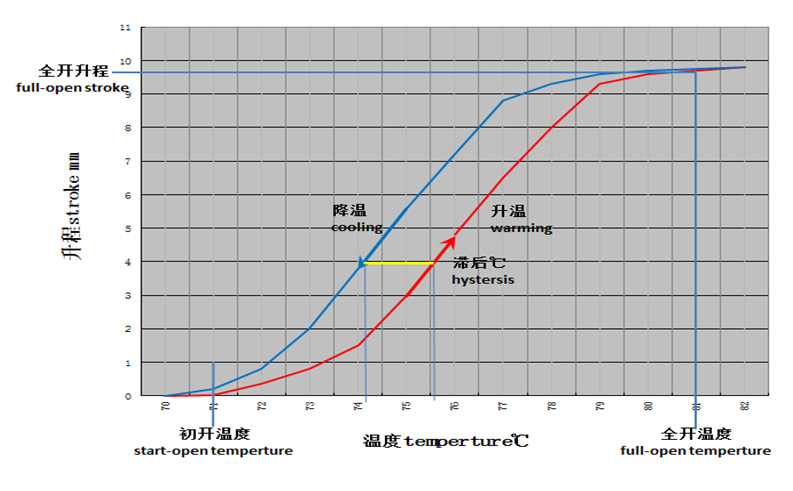
Want to book more products, you are welcome to order!